Time division Multiplexing (TDM)
Definition: "Time-division multiplexing (TDM) is a method of transmitting and receiving independent signals over a common signal path by means of synchronized switches at each end of the transmission line so that each signal appears on the line only a fraction of time in an alternating pattern".
TDM –PAM
 |
TDM –PAM |
Frame synchronization in TDM
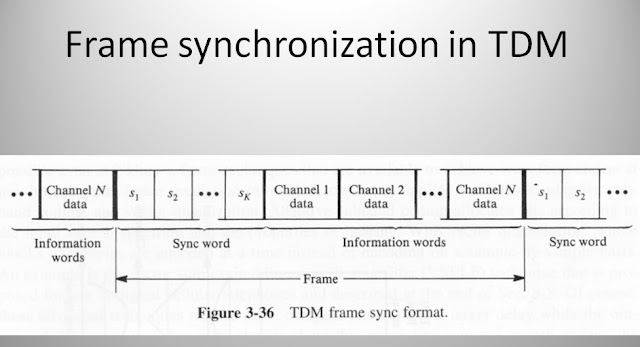 |
Frame synchronization in TDM |
Statistical TDM
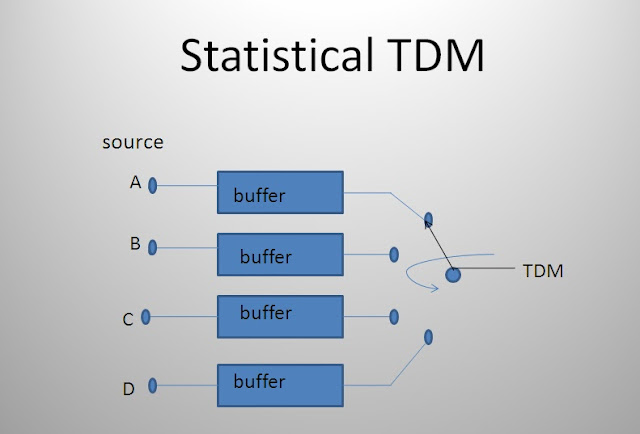 |
Statistical TDM |
Statistical TDM (frame format )
 |
Statistical TDM (frame format) |
Synchronization in TDM system
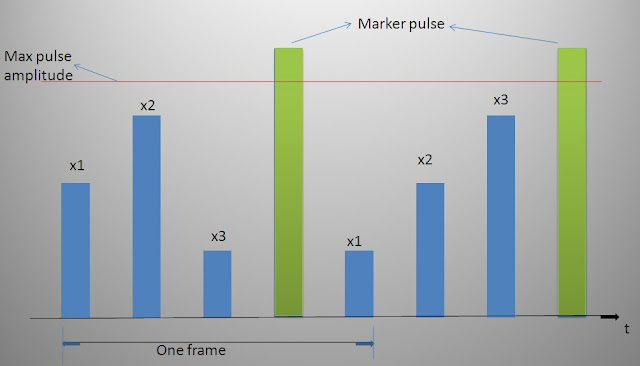 |
Synchronization in TDM system |
#Advantages of TDM:
•Full
available channel bandwidth can be utilized for each channel .
•Inter-modulation distortion is absent .
•TDM
circuitry is not very complex .
•The
problem of crosstalk is not severe .
#Disadvantages of TDM:
•Synchronization
is essential for proper operation .
•Due
to slow narrowband fading , all the TDM channels may get wiped out .
#Applications of TDM:
•For
multiplexing of digital signal .
•For
multiplexing of digitized speech signal
( PCM-TDM TI multiplexing) .
•Statistical
multiplexing .
#Difference Between TDM(Time division Multiplexing) and FDM(Frequency division Multiplexing):
Sr no.
|
FDM
|
TDM
|
1.
|
The signals which are
to be multiplexed are added in the time domain . But they occupy different
slots in the frequency domain .
|
The signals which are
to be multiplexed can occupy the entire bandwidth in the time domain .
|
2.
|
FDM is usually
preferred for the analog signals .
|
TDM is preferred for
the digital
signals .
|
3.
|
Synchronization is not
required .
|
Synchronization is
required .
|
4.
|
The FDM requires a
complex circuitry at Tx and Rx .
|
TDM circuitry is not
very complex .
|
5.
|
FDM suffers from the
problem of crosstalk due to imperfect BPF .
|
In TDM the problem of
crosstalk is not severe .
|
6.
|
Due to bandwidth
fading in the Tx medium , all the FDM channels are affected .
|
Due to fading only a
few TDM channels will be affected .
|
7.
|
Due to slow narrowband
fading taking place in the transmission channel may be affected in FDM .
|
Due to slow narrowband
fading all the TDM channels may get wiped out .
|
Comparison Between FDM Synchronous TDM Statistical TDM:
|
Sr no.
|
Parameter
|
FDM
|
Synchronous
TDM
|
Statistical
TDM
|
|
1.
|
Line utilization
efficiency
|
Poor
|
Good
|
Very good
|
|
2.
|
Flexibility
|
Poor
|
Good
|
Very good
|
|
3.
|
Channel
capacity
|
Poor
|
Good
|
Excellent
|
|
4.
|
Error
control
|
Not possible
|
Not possible
|
Possible
|
|
5.
|
Multi-drop capacity
|
Very good
|
Difficult to
achieve
|
Possible
|
|
6.
|
Transmission
delay
|
Does not
exist
|
Low
|
Random
|
|
7.
|
Cost
|
High
|
Low
|
Moderate
|